Bank statement
Generate a simple bank statement with Carbone
- Template type document docx expert
- Carbone min. v5.0.0+
- Features loop set count aggregator subtotal
- Target bank insurance quote
Overview
Learn how to generate a professional bank statement with these key features:
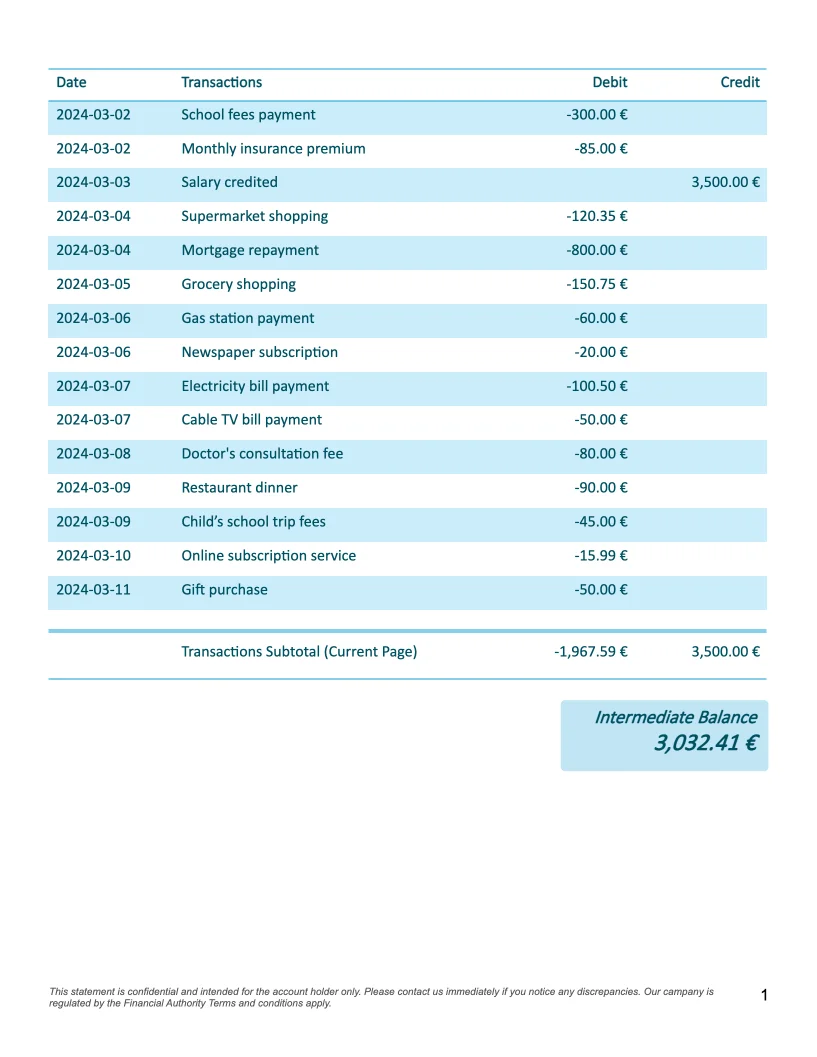
- Display a fixed number of transactions per page
- Show running balance on each page
Step-by-Step Guide
This example demonstrates how to create a bank statement template when your transaction data is stored in a JSON array. We'll show you how to organize the data by page and calculate balances using Carbone's features.
1. Organizing Data by Page
First, we need to structure the data to display a specific number of transactions per page:
- Define how many transactions can fit on one page (for example, 15 lines)
- Calculate which page each transaction belongs to by:
- Group transactions by page number into a new array called
d.groupusing :set:{d.operations[]:set(d.group[id=.numPage].data[])} - Use the new structure to display data in your template:
{d.group[i].data[i].transaction}
Here's how the data structure changes:
Original JSON:
{
"operations": [
{ "transaction": "School fees payment",
"amount": -300 },
{...},
{ "transaction": "Supermarket shopping",
"amount": -130.2 },
{...}
]
}Transformed JSON:
{
"operations": [...],
"group":[
{ "data": [
{ "transaction": "School fees payment",
"amount": -300,
"numPage": 1 },
{...}
]
},
{ "data": [
{ "transaction": "Supermarket shopping",
"amount": -130.2,
"numPage": 2 },
{...}
]
}
]
}2. Calculating Page Subtotals
To show subtotals for debits and credits on each page, use the :aggSum formatter:
- For debits (negative amounts):
{d.group[i].data[].amount:ifGTE(0):show(0):aggSum:formatC} - For credits (positive amounts):
{d.group[i].data[].amount:ifLT(0):show(0):aggSum:formatC}
3. Calculating Running Balance
To display the running balance on each page:
- Combine :aggSum and :cumSum formatters
- Add the opening balance from your JSON:
{d.group[i].data[].amount:aggSum:cumSum:add(...open_bal):formatC}
4. Page Layout Tips
To ensure proper page breaks:
- Insert a page break between pages after displaying all elements
- Remove the final page break to avoid a blank page at the end using this condition:
{d.group[i]..group:len():sub(1):ifEQ(.i):drop(p)}
This formula:
- Gets the current list element with
{d.list[i] - Finds list length with
..group:len() - Adjusts for zero-based indexing with
:sub(1) - Removes the page break if it's the last element with
:ifEQ(.i):drop(p)}
More Examples
Trusted by 800+ paid customers in 40+ countries
Finance
Healthcare
Public
Retail
Industries
Energy
Software
Telecom